Family planning is also known as Birth Control. Family planning is a process that enables individuals to determine the number and spacing of their children and to select the means by which this can be achieved. Family planning is an organized way of preventing unwanted pregnancies.
The following are the purpose of family planning:
FACTS ABOUT FAMILY PLANNING
METHODS OF FAMILY PLANNING
C. Barrier method: This involves the use of condoms. Condom is a thin covering usually made of latex that keeps the sperm from getting into the vagina. For this to be effective, the following must be done;
For a male condom,
For a female condom,
•Women who have ever had cancer of the breast or uterus.
•Women who might be pregnant already
•Women who have very heavy monthly bleeding i.e. monthly bleeding that lasts for more than 8days.
Side effects include: nausea, headache, weight gain,swelling of the breast and variable changes in menstruation patterns
Hormonal methods include:
It is a small sticky patch that releases hormone into the body through the skin to prevent pregnancy. It is more than 99% effective when used correctly. It lasts for a week and should be changed every week for 3weeks and then, have a week off without a patch. It is still effective when sick. It can be worn when swimming, in the bath and while playing sports. It may protect against ovarian, womb and bowel cancer. It doesn’t protect against STIs. Side effects include rise in body temperature, headache, changes in menstrual cycle and blood clotting (rarely).
E.INTRAUTERINE DEVICE:
They are long acting reversible contraceptives (LARC). It is a small flexible plastic device inserted into the uterus. This is inserted and removed by a qualified healthcare provider. The copper IUD provides effective contraception for up to 10years whereas the Mirena levonorgestrel IUD provides 5years protection. It doesn’t interfere with sexual activity and conception is achieved immediately after removal. Side effects include: increased bleeding during menses, dysmenorrhea etc. If a woman already has an STI when an IUD is inserted, that infection can spread to herwomb. Womb infection can lead to infertility or other serious health problems. The IUD can cause a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy if a woman gets pregnant while using an IUD or if she has one put in when she is pregnant. A woman with an IUD must check every month to be sure it is still in place. The best time to check is after monthly bleeding.
F. PERMANENT CONTRACEPTION:
This involves the surgical procedures that permanently prevent pregnancy. In male, it is called vasectomy while in female, it is called tubal ligation. Vasectomy involves surgically severing the vas deferens in both sides of the scrotum. A small cut is made in the upper part of the scrotum, under the penis, and the vas deferens gets cut, tied or blocked. Side effects are pain, infection and hematoma. Vasectomy can sometimes be reversed but reversing a vasectomy isn’t easy and doesn’t always work.
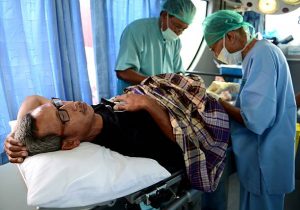
Doctors perform a vasectomy on a Balinese man in Gianyar on Bali island on November 13, 2015. Thousands of men around the world were sterilised in which organisers dubbed a global “vasectomy-athon”, to encourage men to take a bigger role in family planning. (Photo credit: SONNY TUMBELAKA/AFP via Getty Images). Tubal ligation prevents an egg from traveling from the ovaries through the fallopian tubes and blocks sperm from along the fallopian tubes to the egg. The procedure doesn’t affect menstrual cycle. Side effects include bowel perforation, pain, infection, hemorrhage. Tubal ligation cannot be reversed. If reversal is attempted, it requires major surgery and isn’t always effective.
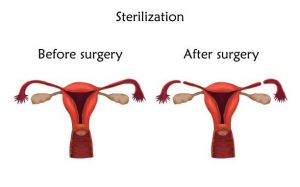
Female sterilization(Tubal Ligation), before and after surgery, illustration(photocredit:gettyimages.com)
G. For people whose religion doesn’t allow the use of the methods mentioned above, they can practise natural family planning. Natural family planning is free, safe and acceptable to many whose religious belief prohibits other methods. It provides an increased awareness of the menstrual cycle and it is useful in helping couples plan pregnancy. To avoid getting pregnant, the woman should abstain from having sexual intercourse 3-4days before ovulation and 2-3 days after ovulation. This is because sperm cells can survive for 2-5days in the woman and once, she ovulates, the eggs released by the ovaries can be fertilised by the sperm.

Aanuoluwapo is a nursing student of Bowen university. She desires to be a caregiver for people and helps to manage physical needs, prevent illness, and treat health conditions.