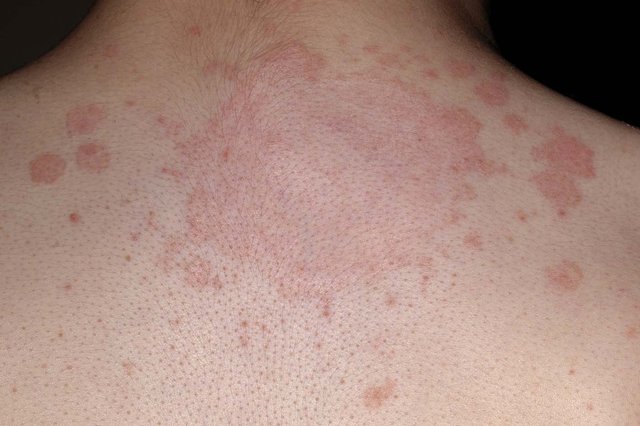
Ringworm (Dermatophytosis or Tinea) unlike its name is an infection caused by a fungus and not a worm. It is popularly called ringworm because it usually has a ring like circular appearance on the skin typically associated with itching. It is more common in warm/tropical regions. It is contagious and can affect both humans and animals. Infection can be from contact with humans, animals, infected objects or infected soil. Also it can affect any part of the body. Ringworm is caused by dermatophytes (fungi of the skin) and they thrive in moist and warm areas of the body.
Types

There are different names given to ringworm depending on the area of the body affected;
1. Tinea Corporis (ringworm of the body)
2. Tinea Capitis ( ringworm of the scalp)
3. Tinea Pedis ( ringworm of the foot in between the toes) it is also known as athletes foot
4. Tinea Cruris (ringworm of the skin around the buttocks, the inner thighs and groin). It is also called jock itch.
5. Tinea Unguium (ringworm of the nail bed) it is also called onychomycosis or fungal nails. It makes the fingernails yellowish, thick and brittle
6. Tinea Manus ( ringworm of the palm and in-between the fingers)
7. Tinea Faciei( ringworm on the face except the beards)
8. Tinea Barbae (ringworm of the bearded areas of the face and neck) also called barber’s itch.
Treatment
With the proper kind of treatment, ringworm affecting the skin can be cured within days or a few weeks while ringworm affecting the nails might take a longer time. If left untreated, ringworm can lead to hair loss, permanent nail damage and the need for a long term use of medications. Also it can spread beneath the skin surface and cause serious illness especially in individuals with weak immune system.
Ringworm can be cured with certain topical creams, oral medications and home remedies. Note that home remedies are only effective for mild cases if symptoms don’t clear after two weeks, seek medical attention. In most cases, your doctor will recommend over the counter creams that contain clotrimazole, ketoconazole, miconazole or terbinafine.
Oral medications used include griseofulvin, fluconazole, itraconazole and so on. The length of time to take the medications depends on the severity of the infection. Also discuss the possible side effects with your doctor.
Prevention
1. Maintain good personal hygiene
2. Don’t share personal items
3. Avoid infected animals
4. Wash your hands after touching animals or soil
5. Do not itch the infected area so as to prevent further spread
6. Do not walk barefoot and if you are an athlete, always keep your equipment clean and we’ll aired
7. If infected, start treatment as soon as possible
IMAGE CREDIT: NHS

Oyewole Ibukun is currently a Medical student of Olabisi Onabanjo University. She has a passion for seeking knowledge with a creative, detail oriented and analytical mindset.