Image credit: pixabay
No matter how careful we are, we cannot totally avoid minor accidents that happen at home. We regularly encounter some minor injuries at home and our inability to properly manage them can lead to complications.
First aid is the initial treatment and care given to an injured person before the arrival of a doctor to stop the injury from worsening; promote recovery, and preserve life. The interval between the injury and the arrival of a doctor is important. This little interval can mean the difference between life, more complications and death.
For this reason, it is important to know some first aid treatment tips.
CUTS
Cuts from sharp objects like blades and knives can occur and cause bleeding. Mild bleeding usually stops on its own while severe bleeding needs to be controlled. Uncontrolled bleeding can cause shock.
 Image credit: pixabay
Image credit: pixabay
STEPS TO STOP BLEEDING
- Cover the cut with cotton-wool or any clean fabric around.
- Apply pressure directly on the wound continuously
- Keep the cut part elevated to reduce blood flow to that area.
For cuts on the hands, raise your hand upward while applying pressure. If the cut is on the legs, put the person on a sitting position and place the leg on an elevated surface.
- For mild bleeding cuts, after the bleeding has stopped, clean with antiseptic liquid like Eusol lotion or dilute Dettol in water.
NB: Avoid using spirit as it would cause the bleeding to start again.
- Then you can apply an antibacterial ointment like penicillin ointment on the cut and then you cover it with gauze and a bandage.
- For severe bleeding, call for help immediately and after the bleeding has stopped, refer to the hospital for further management.
FROM US: To advertise your products and services, click here.
DIARRHEA
Diarrhea occurs when a person passes more than two watery stools within a 24-hour interval. It can be very serious in children because a child’s body is made up of more water than adults.
As a child stools, the child loses body fluid and becomes dehydrated.
Dehydration if not properly managed can be fatal.
First aid treatment for diarrhea in children involves the use Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) and Zinc tablet.
For Preparation of Oral Rehydration Therapy
- Empty a sachet of the Oral
- Rehydration Salts (ORS) into 1litre of clean water.
- Shake gently to mix the salt in water
- Be careful not to overload the child with the solution at once. The ORT should be taken in bits over 24hrs.
After 24hours, the solution should be discarded and another one prepared.
NB: Oral Rehydration Therapy can also be used in adults in cases of severe diarrhea at home before going to the hospital.
FROM US: For your medical check-up at an affordable price, click here. Prevention is better than cure. We conduct medical screenings for individual and organizations at affordable prices. Click here now to learn more.
BURNS
Burns can be caused by fire, chemicals, or electricity. If managed the wrong way can cause permanent damage. Burns can be mild, moderate, and severe which is determined by the size and depth of the burn.
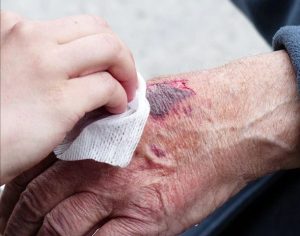 Image credit: pixabay
Image credit: pixabay
STEPS FOR MANAGING BURNS AT HOME
- The first step to managing burns at home is to remove the source of the burn.
- Cool running water should be applied on the part that is affected continuously for about 10minutes
This is essential to reduce the effect of the burning process.
- For mild burns, apply a light gauze bandage to allow air pass through.
- For moderate and severe burns, refer immediately to the hospital.
- Avoid tampering with any blisters formed and take pain relief medications when necessary.
FEVER
Fever is an increase in body temperature which shows that the body is fighting off infections. The normal body temperature is between 36.5°C and 37.4°C. Any body temperature higher than the normal body temperature can be considered as fever.
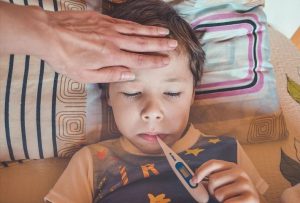 Image credit: pixabay
Image credit: pixabay
When you encounter someone with fever, the following tips are helpful.
- Encourage them to stay in bed and rest
- Give more fluids to keep them hydrated
- The use of light blanket is necessary if there are chills, but they should be dressed in light clothing.
- Give analgesics like acetaminophen (paracetamol) and ibuprofen to reduce fever
NOTE: Take note of proper dosage of the drug. Do not give children and teenagers aspirin.
- Tepid sponge baths
Tepid baths involve soaking a napkin in lukewarm water; using the damp napkin, sponge the person’s forehead, the armpits, chest, back and groin area to reduce the body’s temperature.
FROM OUR MEDICAL TEAM: Do you have any health issue? Click here to chat with one of our doctors. Immediate response guaranteed!
FEBRILE CONVULSIONS
This happens mainly in some children between 6 months to 5 years who have high fever up to 39°C. It is a usually scary experience, but it is self-limiting, that is, it stops on its own.
During febrile convulsion, a child may have jerking movements, twitching, and shaking, convulse and become unconscious.
CARE TIPS
- Place the child on a soft surface and remove any objects within a close range.
- Prevent choking by placing the child on his side
- Don’t restrict the child’s movement or attempt to pad between the teeth
- Make sure to loosen any tight clothing on the child’s neck
- Check for and monitor the child’s vital signs such as pulse rate, breathing pattern and the color of the skin.

Ezike Nonye is a Pharmacist who completed her Bachelor degree from University of Lagos (B.Pharm). She is currently exploring digital marketing analytics as a novel field in Pharmacy practice while also interning at the Federal Medical Center (FMC) Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria. She is a graphic designer, a blogger and an entrepreneur. She is passionate about creating new things from nature and believes that there is no limitation to what you can achieve. She is a Christian and loves writing and open to new ideas and skills.