Sleeping sickness is a disease caused by infection with trypanosoma parasite. Humans get this disease from bites from tsetse fly which has been infected from other infected humans or animals. This disease is caused by two subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei namely; Trypanosoma brucei gambiense in West and Central Africa, and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in East Africa.
Sleeping sickness poses threat to life and mostly affects poor rural populations, causing significant harm. People who travel to endemic regions may also be at risk of getting infected.
This disease affects the brain and if proper care is not given could result in lethal conditions and eventually death.
Symptoms of African Trypanosomiasis
A person infected with Trypanosomiasis will begin to show symptoms about 1-3 weeks after exposure. Some of the symptoms are;
1.Fever
2.Headache
3.Muscle and joint aches
4.Skin rash
5.Confusion
6.Personality changes
7.Weight loss
8.Progressive confusion
9.Difficulty in walking and talking
10.Sleeping for long periods during the day
11.Difficulty in sleeping at night
12.Slurred speech e.t.c.
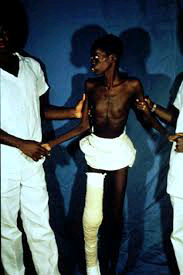

Complications of African Trypanosomiasis
The following are complications of Trypanosomiasis if not handled properly;
1.Anemia and body weaknesses
2.Severe weight loss
3.Aspiration pneumonia (pneumonia due to the inhalation of foreign materials like food particles or vomit into the bronchus)
4. Seizures
5.Stupor or coma (sleeping sickness),
6.Psychosis (emotional and behavioral disorder)
7.Death
Prevention of Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis is a preventable disease though as of present, there is no known vaccine for it. Some measures to prevent it include;
1.Mass screening in tsetse fly endemic areas which may need to be repeated at regular intervals
2.Wearingof long sleeved shirts and trousers to prevent bites from the insect
3.Use of insecticides
4.Bushes around villages and compounds should be cleared.
Treatment
Treatment given depends on the form of the disease and the disease stage. There is better prospect of cure if the disease is identified early. The evaluation of treatment outcome demands that the patient should be followed up for about 2 years and it involves clinical assessment and laboratory examination of body fluids. Some of the drugs used are; Pentamidine, Suramin, Malarsoprol e.t.c.
References:
https://emedicine.medscape.com
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trypanosomiasis-human-african-(sleeping-sickness)
Gbenga Ogunbayode is currently a medical student of Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ogun State, Nigeria. He has earned a certificate of achievement for COVID-19 : Psychological First Aid in Africa from Public Health England and London school of hygiene and tropical medicine. He is a reader, aspiring researcher, lover of music and enthusiastic about knowing more.

